It is a chronic disease of the veins, which is characterized by a thinning of their walls, the expansion of the lumen, and also by the formation of nodes. Occurs in 40% of women and 20% men.
It is a dangerous disease mainly because of their complications. When the wrong or late treatment develop such terrible diseases, such as thrombosis and thrombophlebitis, and bleeding from the dilated veins.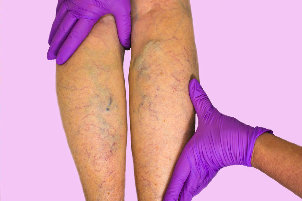 Thrombosis (complete or partial closure of the lumen of a vein clot) or thrombophlebitis (inflammatory disease of the vascular wall in thrombosis) arises suddenly, is not associated with a physical load. The swelling spread rapidly on the lower extremities and is accompanied by the arching of the pain. It may cause redness or blue, local soreness of the skin. In case of interruption of the clot, with the flow of blood gets into the blood vessels of the lungs, and in the case of full or partial closure of the container is able to cause severe disease - thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery. It is a complication often deadly. When a suspected data complications it is necessary to immediately adopt a horizontal position, lift your legs up, the telephone to contact medical help. Injuries in the area of the dilated blood vessels can cause profuse bleeding. In this case it is necessary urgently to save the leg higher location of the bleeding, a tourniquet (medical or improvised), strongly enough, that the bleeding has stopped and urgently call a team of emergency medical services.
Thrombosis (complete or partial closure of the lumen of a vein clot) or thrombophlebitis (inflammatory disease of the vascular wall in thrombosis) arises suddenly, is not associated with a physical load. The swelling spread rapidly on the lower extremities and is accompanied by the arching of the pain. It may cause redness or blue, local soreness of the skin. In case of interruption of the clot, with the flow of blood gets into the blood vessels of the lungs, and in the case of full or partial closure of the container is able to cause severe disease - thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery. It is a complication often deadly. When a suspected data complications it is necessary to immediately adopt a horizontal position, lift your legs up, the telephone to contact medical help. Injuries in the area of the dilated blood vessels can cause profuse bleeding. In this case it is necessary urgently to save the leg higher location of the bleeding, a tourniquet (medical or improvised), strongly enough, that the bleeding has stopped and urgently call a team of emergency medical services.
Weakness of the muscle layers of the inflammation of the walls of the kidney and the valve apparatus are the reason that under the influence of the actions of the "muscle pump", the blood starts to flow in the opposite direction, down. This leads to increased pressure on the walls of blood vessels, further progression of the failure of the valves, the expansion of the lumen of the vein and the formation of knots. Muscle fibers inflammation of the vascular atrophy, disturbed nerve receptors, which regulate venous tone, which, in turn, even more intensifies the manifestations of venous insufficiency. Risk factors for the development of the disease are: hereditary predisposition, pregnancy, obesity, daily prolonged sitting or standing, activities related to lifting weights, the systematic wearing of tight clothing, corsets, unhealthy diet with insufficient content in the diet fiber and vitamins, disorders of the hormonal status.
Clinical manifestations
The main visible sign of the varicose disease of the SAC or cylindrical enlargement of the superficial veins. Varicose veins on the legs are branched, protrude above the surface of the skin in the area of the lower limbs and feet. The maximum varicose nodes expressed after a hard or long physical burden. In the early stage of the disease troubled by increased fatigue, feeling of heaviness in the legs, burning, rupture, the severity of which is at its maximum after physical exertion. You may experience temporary swelling, gnawing pain in the course of the vein. Timely appeal to the specialist even at the initial stage will prevent further development of the disease. When the progression of the disease consists of chronic venous insufficiency.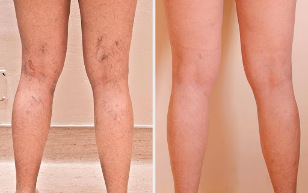
The diagnosis of varicose veins
The "gold" standard of diagnosis is considered to be the ULTRASOUND of the veins of the lower extremities, which will determine the affected area of the veins. On this principle is built the anatomical classification of the varicose disease with an indication of the modified container. For example, the defeat of the large subcutaneous veins beneath or above the knee, a small subcutaneous vein. When questionable data, non-invasive methods resort to surgical methods of research, such as phlebography (intravenous administration of contrast substance in order to assess the condition of the venous system).
Treatment of varicose veins
Non-surgical treatment of varicose veins of the lower extremities, which gives good results only in the debut of the disease with skin manifestations is not strongly expressed and only slightly reduce the performance.
It is a surgical disease, complete cure from which is possible only after the surgical treatment:
- Phlebectomy - operative removal of varicose-expanded veins. The goal of surgery is removal of the defective discharge of blood by removing the main trunks of large or small subcutaneous vein, and also ligation of communication veins. We distinguish several types of operations. They are applicable practically always, even in complex cases. In all these methods, it is removed from vienna, which is the affected and healthy segments of the vein are stored. Vienna as if to gently exfoliate, and not cut out of the fabric, which also reduces the surgical trauma. The same thing happens when using surgical techniques, and, in addition, when it is less bruising because the cooling spasm reduces bleeding.
- Hardening - an introduction to dilated veins special chemical (sclerosant) that causes the "sticking together" the walls of the vein with interruption of the blood flow through it. Consequently, lacking an abnormal discharge of blood, is excluded, cosmetic defects, such as vienna subside and becomes invisible. Sclerotherapy is effective only when the expansion of the small branches of the main trunks, which limits its use in the great severity of the process. The advantage of sclerotherapy is the lack of scarring, the need for hospitalization. After the sclerosing of the vein-specific rehabilitation is not required.
- Laser coagulation - a method based on the destruction of the walls of the vein through the warm impact of the laser, thereby becoming a "spike" of the venous lumen. Appears only when the expansion of the veins more than 10 mm. The method is associated with the course of anesthesia. Cosmetically preferable, but how and after the removal of the vein requires timely activation of the patient, as well as a long elastic compression.